The Naturalium
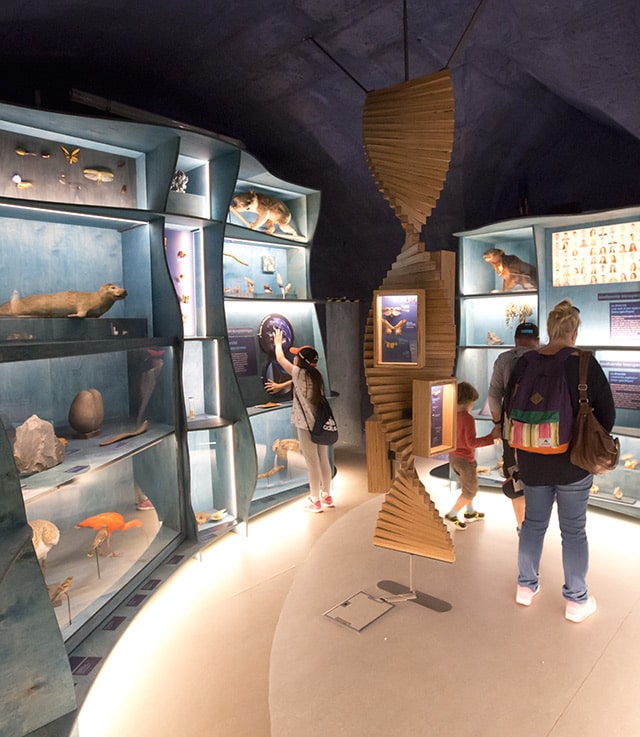

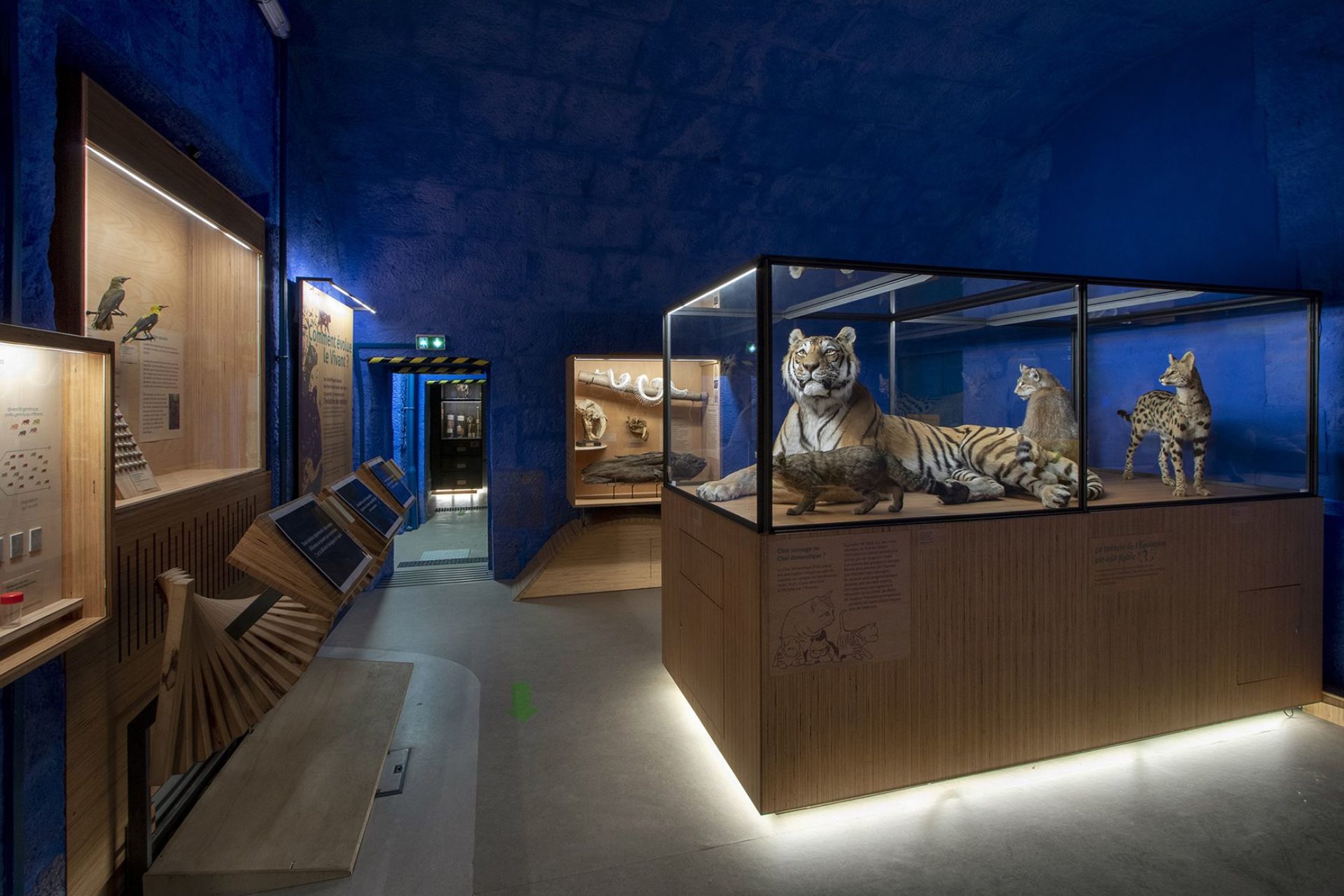
Located in the heart of the Besançon Citadel, on the first floor of what was once the officers' building in Vauban's time, the Naturalium comprises six exhibition rooms with a total surface area of 175m2, dedicated to major themes that provide a better understanding of the notion of biodiversity and its challenges:
- Room 1:
Living diversity: what is biodiversity? - Room 2:
Classifications and relationships between species: all related, all different? - Room 3:
The drivers of biodiversity: why and how is it changing? - Room 4:
The balance of ecosystems: one balance, many balances? - Room 5:
Small gestures, big effects: threats to biodiversity. - Room 6:
History of biodiversity and science in question:
Biodiversity research today.
Collection overview
The missions of the Natural History Museum
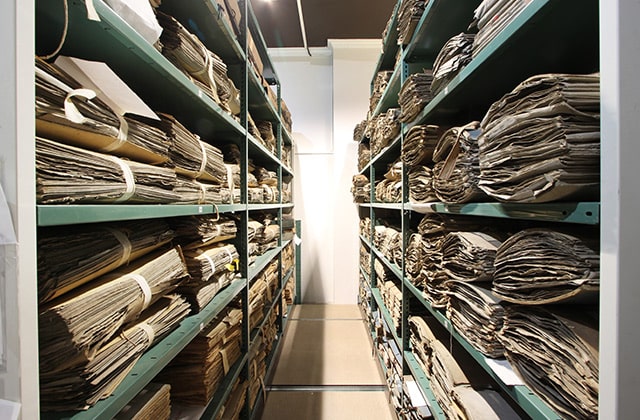

The Muséum de Besançon is first and foremost a Musée de France: responsible for conserving over a million specimen collections, it contributes to research, the dissemination of knowledge and the promotion of the scientific and natural heritage it is responsible for, in order to pass it on to future generations. Today, its ancient collections feed databases that help us better understand the evolution of geodiversity and animal and plant biodiversity.
Finally, it is an atypical establishment, both in terms of its close historical links with the Université de Franche-Comté, and in terms of the wide range of fields it covers (botany, geology, paleontology, entomology, osteology, history of science and science education, etc.).
So many riches that make it a place :
- Conservation, study and research, in close collaboration with teachers, researchers and volunteers (who are actively involved, for example, in the preservation and dissemination of our heritage herbariums);
- Enhancing the value of its collections: although the Museum currently exhibits only a tiny proportion of its collections, sometimes because of their fragility, their dissemination is encouraged by digital projects (such as the RéColNat portal). The Museum regularly contributes to projects with scientific and cultural establishments in Burgundy-Franche-Comté and the Jura Arc;
- Popularizing science and raising visitors' awareness of the need to respect the environment and preserve biodiversity: as a gateway to understanding life and its evolution, its mediators work daily in close collaboration with institutions (national education, museums, etc.) and associations (environmental education and sustainable development network).